CarInsurance.com Insights
Top three factors that drive your car insurance costs:
- Driving record: Tickets and accidents can raise rates by 37% and 57%, respectively.
- Age and experience: Young drivers under 25 and seniors over 70 typically pay the most.
- Where you live: ZIP code risk factors like theft, traffic and weather make a big difference.
Some factors – such as your location, vehicle make/model, age, credit and driving history – can dramatically impact how much you pay for car insurance. Others, such as whether you’re married and your gender, aren’t as important. Still, they add up to how much it costs to protect yourself with an auto insurance policy.
Here is the list of the most important factors that affect car insurance rates:
- Age
- Driving history
- Credit score
- Address
- State of residence
- Vehicle year, make and model
- Annual mileage
- Tickets and violations
- At-fault accidents
- DUIs or license suspensions
- Claims history (yours and on the car)
- Coverage levels (liability-only vs. full coverage)
- Deductibles
- Policy limits
- Bundles and multi-car policies
- Discounts available
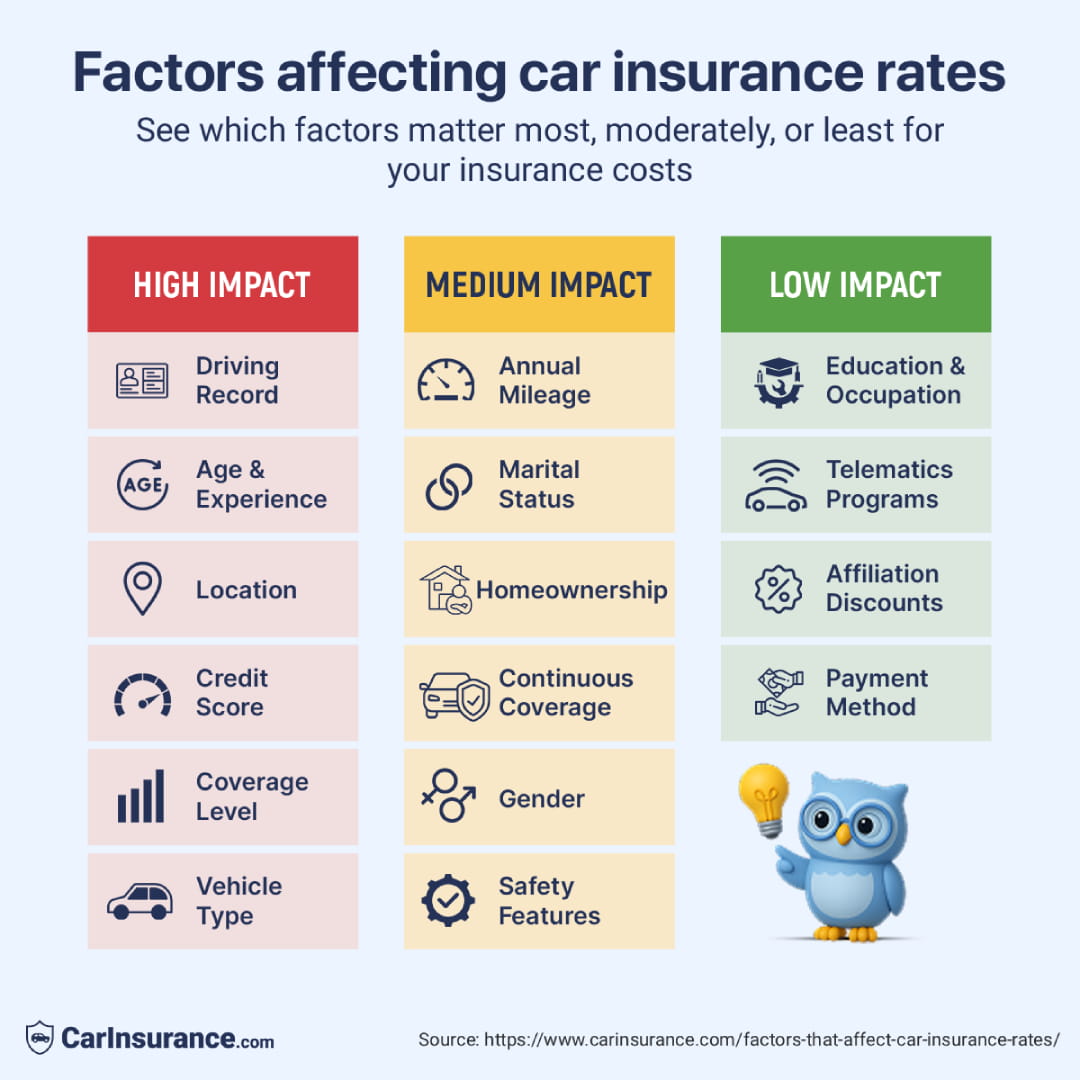

Personal profile: Factors that affect your auto insurance rate
Car insurance premiums depend on a variety of personal factors. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common factors and explain how each one impacts the cost of your car insurance.
1. Age
Your age impacts your premium, especially if you are a teenager or are 75 or older. According to the CDC, car insurance for those younger than 25 is expensive because teenage drivers are almost three times more likely to be involved in a fatal crash than older drivers.
See the table below for the average annual and six-month rates for full coverage car insurance by age group.
| Age group | Average annual rate | Average six-month rate |
|---|---|---|
| Teens (16-19) | $5,613 | $2,806 |
| Young adults (20-24) | $2,976 | $1,488 |
| Adults (25-60) | $1,903 | $952 |
| Seniors (65-75) | $1,864 | $932 |
Age is a high-impact factor: Young and inexperienced drivers face higher rates; premiums typically decrease in middle age, then rise again for seniors. Gender and marital status are medium-impact factors: Married drivers often pay slightly less because they’re considered lower risk.
Some states – Hawaii and Massachusetts – don’t allow auto insurance companies to use age to determine insurance premiums.
2. Driving history
Here’s where your driving experience comes in. Young drivers with limited experience will pay higher rates than drivers with more experience. Additionally, suppose you have accidents or speeding tickets on your record. In that case, you’ll pay more for insurance – rates can increase 19%-64% for a speeding ticket.
Driving record is a high-impact factor: Accidents, speeding tickets and DUIs raise premiums significantly.
3. Credit score
When you apply for an insurance policy, the insurer will check your credit history and use the information on your report to predict whether you’ll likely file claims. The most important factors for a good credit score (for insurance) are a long credit history, minimal late payments and open accounts in good standing.
Note that the following states prohibit credit from determining premiums: California, Hawaii, Massachusetts and Michigan.
Credit score (where allowed) is a high-impact factor: A strong credit history lowers rates, while poor credit can add hundreds of dollars per year.
Car insurance costs 117% more for drivers with bad credit than those with good credit. Improving your credit score can lower your premium over time.
2. Address
Where you live (and park your car) will directly impact your insurance premium. Of all the factors that affect car insurance rates, this is one of the most critical factors affecting your insurance rate. To assess your risk, insurers study crime rates, neighborhood densities, the number and severity of claims made annually and even the weather.
You will pay more for car insurance if you live in an area with high accidents and theft/vandalism or are prone to severe weather damage. And don’t forget that if you move, your rates could change – see how much they’ll change with this moving calculator.
Here’s an example of how car insurance premiums differ based on your city and insurance company.
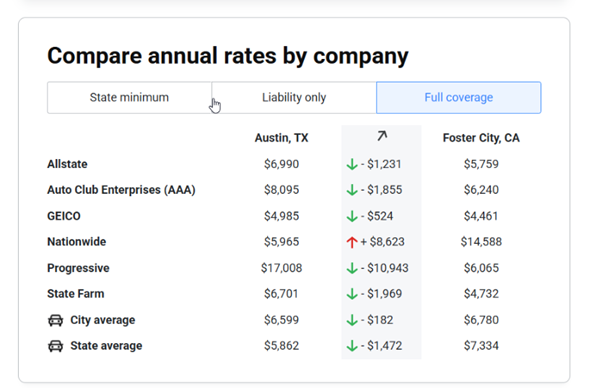
Location (ZIP code) is a high-impact factor: Living in an area with high accident rates, theft or severe weather increases costs.
Your location: How your ZIP code affects your rates
Where you live — and where you park your car — matter more than you think when it comes to car insurance prices. Not only do premiums differ by state and city, but premiums can also vary between ZIP codes in the same city.
“Insurers are focused on assessing risk when determining rates and certain ZIP codes pose a greater risk due to crime, accidents, population density, weather and average claims history, which are all factors that can affect risk level and ultimately, insurance premiums,” says Justin Yoshizawa, director of product management at Mercury Insurance.
Learn more about how where you live can affect the cost of your auto insurance policy.
5. State of residence
In some states, even the mandated minimum coverage includes uninsured motorist coverage or personal injury protection insurance, making insurance pricier than in a state where those aren’t required. Additionally, whether your state is a no-fault or tort state will affect how much you pay for car insurance.
State-specific rules
Your state’s unique car insurance laws and requirements can impact car insurance premiums. For example, Michigan drivers pay some of the highest car insurance rates due to the state’s no-fault laws. If you live in a state with lower minimum coverage requirements, you might pay less for auto insurance.
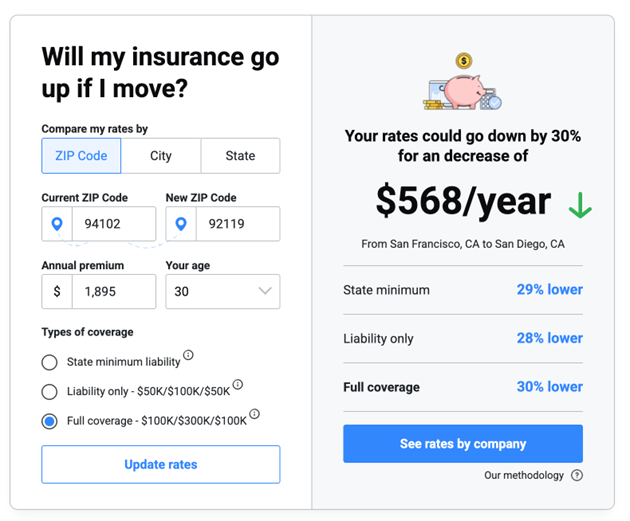
How moving can impact car insurance premiums
If you’re moving, your car insurance premium might change. Depending on your new location, your rate could be higher or lower than your previous premium. For example, if you’re moving from San Francisco to San Diego, California, your premium would decrease by 30%.
Your vehicle: What you drive influences what you pay
The type of vehicle you drive can significantly impact the cost of your car insurance.
“High-end sports cars, luxury cars and some electric vehicles (EVs) have higher premiums due to their parts costing more to repair or replace after an accident. An EV battery, for example, can cost thousands of dollars to replace if damaged,” Yoshizawa says. “On the other hand, cars with strong safety ratings, lower repair costs or advanced safety features often cost less to insure.”
Here’s a closer look at how your car’s profile impacts your car insurance cost.
6. Vehicle year, make and model
Insurers will consider the car model’s claims record and the type of car you drive will impact how your insurance rate is determined. Smaller, safer cars are cheaper to insure, whereas luxury vehicles with high-end technology and expensive finishes will be expensive.
Vehicle type is a high-impact factor: Expensive, high-performance or hard-to-repair cars cost more to insure than safe, affordable models.
For your vehicle model, car insurance companies look at the following:
- Purchase price
- Theft rate
- Cost of repairs
- Accident rate
- Safety tests
Car insurance companies also consider the types of safety features your car has. So, if your car has airbags and brake stabilization, you may pay less for insurance. However, cars with high-tech safety features, such as collision-warning systems, may add to the insurance price if the cost to repair or replace the feature is expensive.
Vehicle safety features are a medium-impact factor: Anti-theft devices, lane assist and crash-avoidance systems may lower rates.
7. Annual mileage
The more you drive, the higher your chance of getting into an accident. That’s why insurance companies consider how much you drive when setting insurance rates. You’ll pay more if you have a long commute or log many miles because you are considered a higher risk.
The type of miles you put on your vehicle can also be factored into your premium. For example, you might pay less for car insurance if you use your vehicle for pleasure, rather than commuting. If you drive infrequently (less than 8,000 miles per year), you might qualify for a low-mileage discount. You can also consider a pay-per-mile policy, which may be cheaper than traditional car insurance.
Annual mileage is a medium-impact factor: Driving more miles increases risk exposure; low-mileage drivers may qualify for discounts.
Your driving history: Your track record follows you
Of all the factors that impact your car insurance premium, your driving history is one of the most important. Drivers with a clean record typically pay less than people with a history of speeding tickets, accidents or insurance claims.
For example, drivers pay around 56% more for a property damage accident and 63% more for a bodily injury accident than drivers without an accident on their record.
Your driving record is a high-impact factor: Accidents, speeding tickets and DUIs raise premiums significantly.
In the table below, you can see how certain violations impact average car insurance premiums:
| Violation | Annual full coverage cost | $ increase | % increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 at-fault property damage accident over $2,000 | $2,973 | $1,075 | 57% |
| 1 At-fault property damage accident under $2,000 | $2,952 | $1,055 | 56% |
| 1 comprehensive claim for over $2,000 | $2,243 | $346 | 18% |
| 1 comprehensive claim for under $2,000 | $2,230 | $333 | 18% |
| 2 At-fault property damage accident over $2,000 | $4,238 | $2,340 | 123% |
| 2 comprehensive claims for over $2,000 | $2,505 | $608 | 32% |
| At-fault bodily injury accident | $3,096 | $1,199 | 63% |
| Single vehicle accident (driver’s car only) | $2,964 | $1,066 | 56% |
8. Tickets and violations
If you’ve gotten any speeding tickets or traffic violations in recent years, you will likely pay a higher insurance premium. The exact rate increase depends on factors like the severity of the incident and the type of violation.
For example, a speeding ticket for going 10 mph over the posted limit may have a smaller impact on rates than getting pulled over for distracted driving.
9. At-fault accidents
All car accidents can affect your insurance premium, but you’re more likely to see a rate increase after an at-fault crash. Causing an accident makes it riskier for you to insure, so insurers tend to increase premiums after a collision. The actual rate increase usually depends on the accident’s severity, how much damage was done and what percentage of the fault was yours.
10. DUIs or license suspensions
A DUI is one of the most serious traffic violations; if you get convicted of one, you can expect your car insurance premium to increase considerably. The same goes for other types of license suspensions. For example, if your license gets suspended after a reckless driving incident, your car insurance premium will increase.
11. Claims history (yours and your car’s)
Any claim can affect how much you pay for auto insurance. While at-fault claims will result in higher rates, the number of claims you make is also significant.
If you have made several claims on your policy in a certain period of time, such as three claims in three years, you can expect your car insurance rate to increase. More claims will peg you as a higher-risk driver and raise your premiums for a few years.
Insurance companies typically look back three to five years when setting car insurance premiums. Any accidents, claims or traffic violations from that time will likely impact your insurance premium.
Your policy choices: You have more control than you think
Several policy-related factors can affect your car insurance premium, such as the types of coverage and coverage limits you choose. Here’s what to know about how policy choices can determine your rate.
12. Coverage levels (liability-only vs. full coverage)
The type and amount of car insurance you buy will affect how much you pay.
A state minimum coverage policy with liability-only insurance is the cheapest policy you can legally have, but it offers limited coverage. Liability car insurance coverage includes bodily injury liability and property damage liability if you’re at fault in an accident.
A full coverage policy provides more coverage, but has a higher premium. Full coverage includes collision insurance, which covers damage to your car when it hits another object/vehicle. It also has comprehensive insurance, covering your car for natural disasters, animal strikes, theft and vandalism.
If you add optional policies, like underinsured/uninsured motorist coverage, gap insurance or Personal Injury Protection (PIP), your rate will be higher.
13. Deductibles
If you have full coverage car insurance, you’ll pay a deductible when you file a collision or comprehensive claim. The deductible is the money you pay out of pocket when you have a covered loss. Choosing a higher deductible will result in a lower premium, whereas a lower deductible will have a higher premium.
Coverage levels and deductibles are high-impact factors: More coverage and lower deductibles raise your premium, while liability-only with higher deductibles costs less.
14. Policy limits
The policy limits you choose will impact your car insurance premium. Raising your liability coverage limits beyond what’s legally required is often recommended, but it will increase your rate. If you choose replacement cost value (RCV) coverage for your vehicle instead of the standard actual cash value (ACV), your rate will increase.
15. Bundles and multi-car policies
Most car insurance companies offer a discount to customers who bundle their auto insurance with another policy, like homeowners or renters insurance. Bundling your policies can help you get a cheaper premium.
You can also get a discount when you insure multiple cars on the same policy. So, for example, if you and your spouse have your own car insurance policies, joining policies and insuring both cars on the same one could help you save money.
16. Discounts lower insurance cost
Discounts can significantly reduce how much you pay for auto insurance. The top discounts include good/safe driver, accident-free, student away, good student and discounts for bundling auto and homeowners insurance. Safety features, telematics, professional organizations and autopay can also save you money on your policy.
Policy discounts are medium-impact factors: Multi-car, loyalty or bundling discounts can make a noticeable difference. However, affiliation discounts (AARP, employer groups, military) are low-impact factors, as are discounts for education level, occupation and payment methods.
Other pricing factors for car insurance
Other low- and medium-impact factors that can affect how much you pay for car insurance include the following:
- Marital status (medium impact)
- Education (low impact)
- Occupation (low impact)
- Gender (medium impact; not in all states)
- Homeownership (medium impact)
- Payment method (low impact)
- Telematics/usage based insurance (low impact)
- Vehicle safety discounts (medium impact)
- Continuous insurance history (medium impact)
Like any other major purchase, your auto insurance policy is a big commitment. You can save money on your insurance costs by shopping around when it’s time to renew and by being aware of how to save money on a policy.
Common misconceptions about car insurance
Car insurance is often misunderstood, leading many drivers to make costly mistakes. Let’s clear up some of the most common myths and separate fact from fiction.
Misconception: All car insurance coverage is the same
Many drivers assume that every policy provides the same level of protection, but in reality, coverage varies widely. Liability insurance, which is required in most states, covers damage you cause to others but won’t pay for your car’s repairs. Comprehensive and collision coverage, on the other hand, protect your vehicle against theft, accidents and natural disasters. The amount of coverage you choose, along with uninsured motorist protection or roadside assistance, significantly impacts what your policy covers.
The truth: Not all policies are created equal. Choosing the cheapest option without reviewing coverage details could leave you financially vulnerable in an accident.
Misconception: Staying loyal to an insurer always saves you money
Loyalty can be a good thing, but when it comes to car insurance, it doesn’t always pay off. Many drivers believe sticking with the same insurer for years will automatically result in lower rates. However, some insurance companies practice price optimization — gradually increasing premiums for long-term customers who are less likely to shop around.
The truth: Comparing quotes from different insurers every year or two can help ensure you’re still getting the best deal. Some companies even offer new customer discounts, which can make switching worthwhile.
Misconception: Your car’s color affects your insurance premium
A common myth suggests that red cars are more expensive to insure because they are more likely to be pulled over for speeding. However, insurance companies don’t factor in car color when calculating premiums. Instead, they consider the car’s make, model, year, safety features, theft rate and repair costs.
The truth: A red sports car might cost more to insure, not because it’s red, but because it’s a high-performance vehicle. If you drive a red minivan, your insurance rate won’t differ from a blue or white one.
How to lower your car insurance premiums
There are a variety of ways to reduce your car insurance premium. Here are some tips for saving money on your policy:
- Raise your deductibles: Some car insurance policies, like collision and comprehensive insurance, require a deductible when you file a claim. Choosing a higher deductible will result in a lower monthly insurance premium.
- Improve your credit score: In most states, your credit score can impact your car insurance rate. Boosting your credit score by paying off debt and lowering your credit utilization ratio can reduce your auto insurance premium.
- Pay your annual premium in full: You can typically save money on car insurance when you pay your annual premium upfront and in a lump sum. You might also qualify for savings if you pay biannually.
- Bundle your policies: One of the most effective ways to lower your car insurance premium is to bundle multiple policies, such as car and home insurance. For example, State Farm says customers who bundle their home and auto insurance can save $1,073 on their combined premium.
- Take a defensive driving course: Car insurance companies usually offer savings to customers who complete an approved defensive driving course. This discount can be especially beneficial if you have young drivers in your household.
- Shop around: Car insurance companies charge different rates for the same types and coverage amounts. It’s a good idea to shop around and get quotes from multiple insurance carriers to find the most affordable policy for your situation.
Which rate factors can you control?
Some car insurance factors are in your control and others aren’t. See which factors you’re able to influence and which ones are not.
Controllable factors
- Policy types
- Coverage level
- Deductibles
- Driving behavior
- Credit score (over time)
- Discounts
Uncontrollable
- Age
- Gender
- ZIP code (unless you’re moving)
- State insurance laws
- Weather, theft and vandalism rates in your area
- Industry-wide rate adjustments
You can influence five of these factors. See how adjusting them could change your rate.
Calculate car insurance rates by ZIP code
Rates vary by location. Our tool helps you understand how your ZIP code impacts your premium.
For 30 year old Male ( Full - 100/300/100)

Why your car insurance rate isn’t just about your driving record
Your driving record is essential, but it’s only one of many factors insurers use to set your rate. Insurance companies look at the whole picture to predict how likely you are to file a claim.
Even with a clean driving record, your rate can vary based on these other factors. Understanding them helps you shop smarter and find ways to save.
Here’s what else matters:
- Location: ZIP codes with higher accident rates or theft can mean higher premiums.
- Vehicle type: Expensive or high-performance cars cost more to repair or replace.
- Coverage choices: More coverage or higher limits increase your cost.
- Deductible: A lower deductible raises your premium.
- Age and experience: Younger or new drivers typically pay more.
- Credit history: In most states, insurers use credit-based scores to assess risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often do insurance companies re-evaluate my premium and what triggers a change?
Car insurance companies re-evaluate insurance premiums during the policy renewal period, which usually happens once per year. Things that can trigger a rate adjustment include changes to your credit score, claim history, vehicle type, home address and the number of drivers on your policy.
Do discounts significantly lower car insurance premiums?
Yes, car insurance discounts can significantly reduce your premium. However, some discounts are more effective at lowering your premium than others. For example, bundling multiple policies often results in a larger discount than paying your annual premium in full, and each insurer’s discounts vary.
How do insurance companies determine if a vehicle is too risky to insure?
Insurance companies consider several criteria to determine risk, including vehicle make and model. For instance, an insurer may determine that n expensive sports car is too risky to insure.
Why did my car insurance go up if I haven’t had an accident?
Even without an accident, your rate may rise due to statewide cost increases, inflation in repair costs, more severe weather events or changes in your ZIP code’s risk profile. Insurers adjust premiums based on overall claim trends.
Does credit score really affect car insurance rates?
Yes. In most states, drivers with poor credit pay significantly more than those with excellent credit. A strong credit history signals financial stability, which insurers link to fewer claims.
Do gender and marital status still impact car insurance?
Yes, but less than in the past. Gender is not allowed as a rating factor in some states, while in others men (especially young men) may pay slightly more. Married drivers often receive small discounts compared to single drivers.
How much does one speeding ticket increase insurance costs?
A single speeding ticket can raise your premium by 37%, depending on your insurer and state. Multiple tickets or serious violations like DUIs cause much larger increases.
Does the car I drive really change my insurance rate?
Yes. Cars that are expensive to repair, easy to steal or built for high performance generally cost more to insure. Vehicles with good safety records and lower repair costs, like many SUVs and minivans, tend to be cheaper.
Can I lower my insurance rates if I drive less?
Yes. Many insurers offer low-mileage discounts or usage-based programs. If you drive fewer than 7,500–10,000 miles per year, you may qualify for a lower rate.
How can I control my car insurance costs?
You can lower costs by maintaining a clean driving record, improving your credit score, choosing a safe, reliable vehicle, raising deductibles and shopping around for quotes at least once a year.
Resources & Methodology
Sources
- Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. “Teen Drivers.” Accessed December 2025.
- Insurance Information Institute. “Facts + Statistics: Uninsured motorists.” Accessed December 2025.
Methodology
CarInsurance.com commissioned Quadrant Information Services to get car insurance rates. The rates are based on the sample profiles of 40-year-old male and female drivers carrying full coverage policies with limits of 100/300/100 and $500 collision and comprehensive deductibles. Read the detailed methodology for more information.
Get advice from an experienced insurance professional. Our experts will help you navigate your insurance questions with clarity and confidence.
Browse all FAQs
